|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Anti-Aging Solution
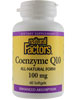
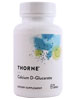
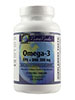
By Marcia Zimmerman, C.N. Our biological clock starts ticking at birth. Until 30 or so, we generally grow better as we age, and most tend to be well beyond 30 before beginning to experience signs of aging, which include skin wrinkling, hair graying, aches, pain, fatigue, reduced stress adaptation, lowered immunity, and vision loss. Though we may have to accept growing older, we don't have to accept these signs as part of the aging process. WHY DO WE AGE? Free radicals are the primary cause of aging. These highly charged atoms, molecules, or compounds are missing one electron, making them unstable. Electrons normally pair up, but if enough external energy is supplied, i.e., ultraviolet light, one of the paired electrons may be "knocked off." An atom with a single electron seeks a second, which it steals from a neighboring atom that must now gain its own electron. The process of electron swiping disrupts normal cellular processes, wreaking havoc and damaging cells. Electrons are easier to steal from some molecules, with DNA, fatty acids, and proteins--like those that comprise muscles and organs--being prime targets. So how can we better help the body help itself? Since genetic expression can be moderated by our environment, this establishes a clear cause and effect between aging conditions, diet, and lifestyle. Consequently, you can take charge of your own aging process. The Anti- Aging Solution provides five steps that attack aging at its genetic roots by preventing free-radical damage to DNA, enhancing its repair, and reigning in runaway inflammation. STEP 1 Lower cortisol by reducing stress Cortisol--dubbed the age-accelerating hormone--affects every cell of your body and nervous central system, activating protective defense mechanisms to save your life. However, persistent elevation of cortisol, usually resulting from induced stress, disrupts homeostasis by interfering with hormone, immune, brain, and nerve function. High cortisol levels are directly related to: • Collagen and elastin protein breakdown in skin, joint, bone, and muscle tissue • Memory loss and nervous system damage • Increased inflammation due to allergies, asthma, and arthritis Taking frequent breaks throughout the day for stress relief through breathing, stretching, relaxation, and meditation will help lower cortisol. STEP 2 Nourish genes by lowering sugar The typical Western diet, which is loaded with white flour and refined sugars, quickly turns to glucose in the body. The ultimate result of a high glucose load is glycation-- oxidized glucose that coats the surface of proteins, such as collagen, preventing them from functioning. Collagen is the most plentiful protein in your body--making up skin, blood, lymph vessels, joints, tendons, ligaments, and internal organs--and the one most affected by glycation. Aging conditions most linked to glycation include: • Memory loss (sugar coating of brain cells) • Clinical depression • Skin wrinkling or sagging • Impaired immune functions (damage to thymus gland, lymphatic tissue, and immune cells) Eating an abundance of fruits and vegetables protects your genes and promotes health and longevity. STEP 3 Exercising your genes Before the 1950s, Americans didn't worry much about getting enough exercise. They walked or rode bikes to work. Many worked long hours on farms or in factories, as did their children. Today, many spend the day in front of a computer, grab something quick to satiate hunger, then go home and watch TV until bedtime. Consequently, our lack of exercise is killing us. Add at least 20 minutes of stretching, strength training or aerobic exercise to your daily routine. STEP 4 Avoid environmental toxins and protect hormone levels Environmental contaminates, such as those found in fertilizers, plastics, herbicides, and wood and carpet materials, are called endocrine disrupters, which affect hormones in both men and women. According to Theo Colborn of the World Wildlife Fund in Washington, D.C., "Endocrine-disrupting chemicals can undermine neurological and behavioral development and subsequent potential of individuals exposed in the womb...It may be expressed as reduced intellectual capacity, impaired responsiveness to environmental demands, or a variety of other guises." STEP 5 Supplementing genes Even with a dramatic change in diet, supplements containing concentrated forms of nutrients, usually from food sources, are needed to overcome the damaging effects of micronutrient deficiencies, pollution, radiation, and internally generated free radicals. Since vitamins and minerals are required to cofactor metabolic enzymes, micronutrient deficiencies can cause profound alterations in normal cellular function. Nutraceutical supplements can also amp up DNA repair capability--the bottom line in preventing most disease by reducing DNA damage. KEY SUPPLEMENTAL NUTRIENTS SULPHUR-CONTAINING ANTIOXIDANTS Cruciferous vegetables contain a family of sulfur compounds known collectively as glucosinolates, and include diindolymethane (DIM), sulforophane, calcium D-glucarate, and indole-3-carbinol (I3C). They have been standardized in extracts and numerous trials validate their anti-aging benefits, such as detoxification and hormone balancing. MITOCHONDRIA DNA PROTECTORS Oxidative damage to the mitochondrial DNA is the root of aging and its conditions. Coenzyme Q10 and alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) provide the most powerful protection. CoQ10 inhibits lipid oxidation in cell membranes, including the brain, and protects DNA from oxidative damage. It also stabilizes membranes and reconstitutes vitamin E as an antioxidant. ALA is active in protecting both lipids and aqueous cellular components, and may reverse memory loss by reducing DNA/RNA oxidation. ESSENTIAL FATTY ACIDS From an anti-aging perspective, EFAs alter metabolism, change cellular response, and affect cellular growth and differentiation. Benefits of EFAs are to modulate genetic expression of key metabolic enzymes and reduce DNA damage. Omega-3, 6, and 9s, or various combinations thereof, have been shown to provide cardiovascular, immune, brain, and nerve function benefits, as well as general anti-aging benefits to dry skin, brittle nails, and thinning hair. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||